2.0.0-alpha.9
This release introduces significant additions and improvements related to VerticalAxis, scroll, and zoom.
| Breaking changes | Addressed |
|---|---|
| Moderate | #265, #296, #317, #349, #352, #384, #496, #574, #585 |
If you need any help updating to Vico 2.0.0-alpha.9 please start a discussion in the “Questions” category.
VerticalAxis
We’re introducing two new APIs:
AxisItemPlacer.Vertical.step, which lets you specify the y step betweenVerticalAxisitems or finds the optimal one automaticallyAxisValueOverrider.auto, which uses dynamic rounding
These produce more visually appealing VerticalAxis instances. Consider the following Vico 2.0.0-alpha.8 chart. The data’s maximum y value is 14.94, which results in random-looking VerticalAxis label values:
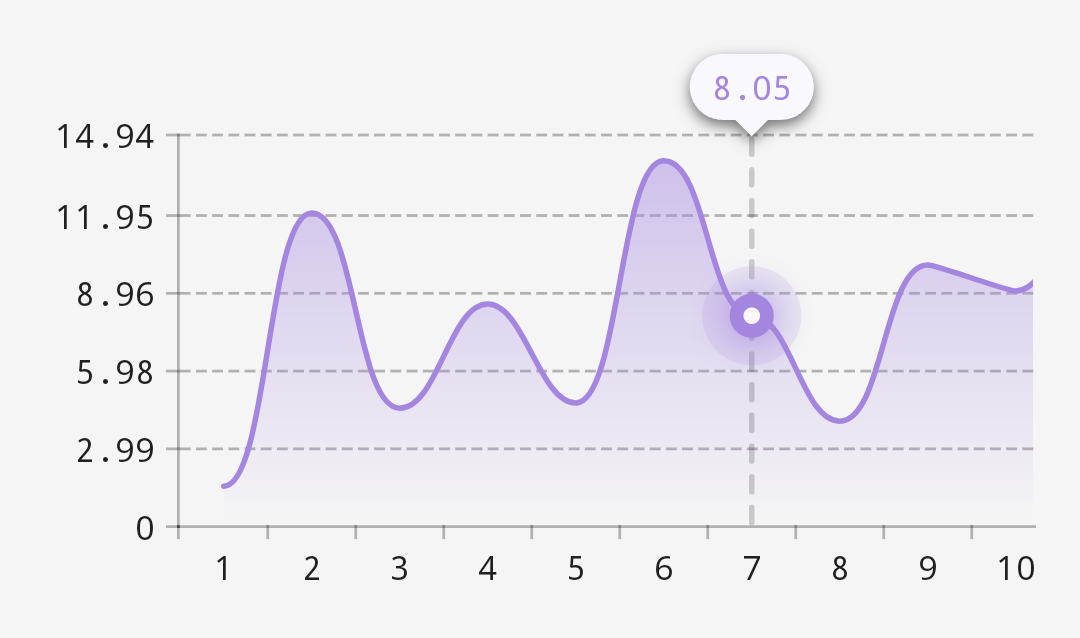
In Vico 2.0.0-alpha.9, with no changes to its code, the same chart looks like this:
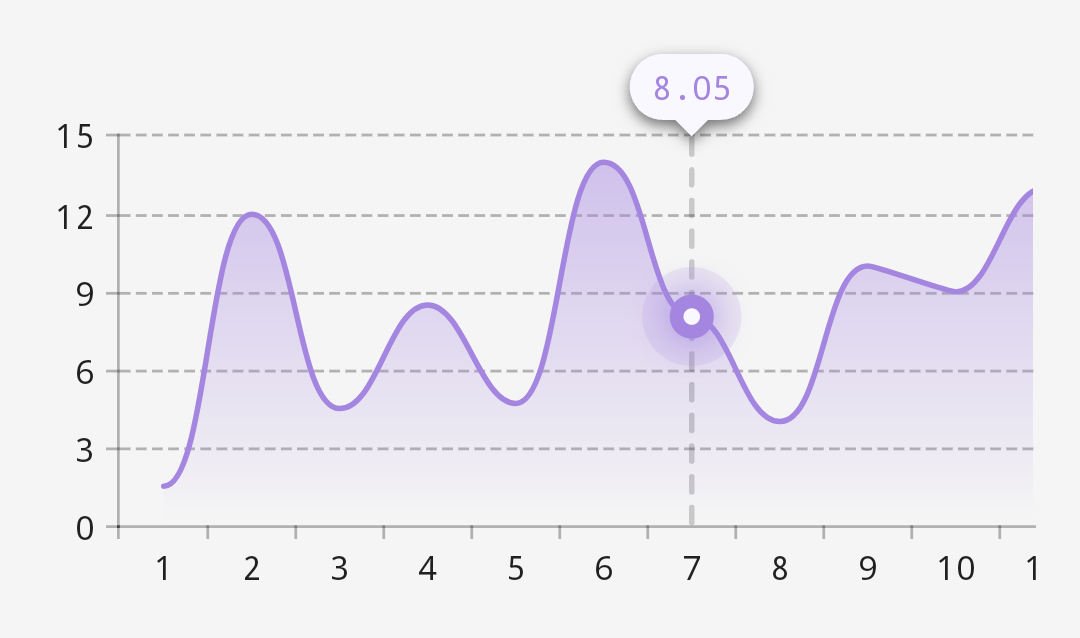
AxisItemPlacer.Vertical.step and AxisValueOverrider.auto are the new defaults. To specify your own y step, use AxisItemPlacer.Vertical.step explicitly. The step lambda receives an ExtraStore.
AxisItemPlacer.Vertical.step({ 5f })
AxisItemPlacer.Vertical.default remains available, but it’s been renamed to AxisItemPlacer.Vertical.count. The count lambda (previously maxItemCount) receives an ExtraStore rather than a ChartValues instance. Thus, to read from the ExtraStore, replace it.extraStore with it. CartesianChartModel-based calculations shouldn’t be performed here, as the lambda is called multiple times. If you’re doing so, switch to AxisItemPlacer.Vertical.step if appropriate, or precalculate the item count, save it as an extra, and read the extra in the lambda.
Each of the four AxisValueOverrider functions now receives the minimum and maximum x or y values rather than the CartesianLayerModel. This is because CartesianLayerModel#maxY isn’t the effective maximum y value for ColumnCartesianLayers with ColumnCartesianLayer.MergeMode.Stacked. ColumnCartesianLayerModel has an aggregateMaxY value, but AxisValueOverriders don’t know which ColumnCartesianLayer.MergeMode is in use. With the new AxisValueOverrider functions, this is no longer an issue. Also, AxisValueOverrider no longer has a type parameter, so universal AxisValueOverriders can be created.
If you’re using one of the built-in AxisValueOverrider implementations, all you have to do is remove any explicitly specified types. AxisValueOverrider.fixed<...>(...) becomes AxisValueOverrider.fixed(...) and so on. If you have a custom AxisValueOverrider, update the function signatures so that they match those in the interface, and replace model.minX with minX and so on.
This is unlikely to affect you, but axisValueOverrider is now a field of BaseCartesianLayer rather than CartesianLayer, and it’s no longer nullable. If you need the behavior that null produced, use AxisValueOverrider.fixed() (with no arguments).
Scroll
The scroll API has been consolidated and expanded. The new Scroll interface represents CartesianChart scroll values or deltas. It has two subinterfaces, Absolute and Relative, both of which have singletons and factory functions in their companion objects. Most notably, Scroll.Absolute.x enables you to scroll to a specific x value and align it as required, and Scroll.Relative.x lets you scroll by an x delta. Other options include Scroll.Absolute.Start, Scroll.Absolute.End, Scroll.Absolute.pixels, and Scroll.Relative.pixels. You can also create your own Scroll implementations.
- Compose
- Views
ChartScrollState is now called VicoScrollState. Instances are created via rememberVicoScrollState. The isScrollEnabled parameter has been renamed to scrollEnabled. The type of initialScroll is Scroll.Absolute—replace InitialScroll.Start with Scroll.Absolute.Start, and InitialScroll.End with Scroll.Absolute.End. There’s also a new autoScroll parameter, which lets you set a different Scroll than initialScroll for automatic scrolling. The default value is initialScroll, which matches the old behavior.
CartesianChartHost(scrollState = rememberVicoScrollState(...), ...)
There are two methods for programmatic scrolling, scroll and animateScroll. Replace scrollBy(...) with scroll(Scroll.Relative.pixels(...)), and analogously for animateScrollBy. Note that listeners have been removed—read the current and maximum scroll values via the value and maxValue fields, which use MutableFloatState. As a final example, here’s how to perform an animated scroll to x = 10 and align it to the center:
animateScroll(Scroll.Absolute.x(x = 10, bias = .5f))
ChartScrollSpec has been replaced by ScrollHandler, which is also responsible for programmatic scrolling. The isScrollEnabled parameter has been renamed to scrollEnabled. The type of initialScroll is Scroll.Absolute—replace InitialScroll.Start with Scroll.Absolute.Start, and InitialScroll.End with Scroll.Absolute.End. There’s also a new autoScroll parameter, which lets you set a different Scroll than initialScroll for automatic scrolling. The default value is initialScroll, which matches the old behavior.
cartesianChartView.scrollHandler = ScrollHandler(...)
There are two methods for programmatic scrolling, scroll and animateScroll. Replace cartesianChartView.scrollBy(...) with scrollHandler.scroll(Scroll.Relative.pixels(...)), and analogously for animateScrollBy. Replace cartesianChartView.scrollTo(...) with scrollHandler.scroll(Scroll.Absolute.pixels(...)), and analogously for animateScrollTo. Whereas CartesianChartView had setAnimatedScrollInterpolator and setAnimatedScrollDuration functions, ScrollHandler#animateScroll has interpolator and duration parameters. ScrollHandler has addListener and removeListener methods. The listener interface is ScrollHandler.Listener. As a final example, here’s how to perform an animated scroll to x = 10 and align it to the center:
animateScroll(Scroll.Absolute.x(x = 10, bias = .5f))
We’ve added state restoration, so CartesianCharts’ scroll values are persisted across configuration changes (e.g., on screen rotation).
Zoom
Like the scroll API, the zoom API has been enhanced. The new Zoom interface represents CartesianChart zoom factors and has singletons and factory functions in its companion object. Zoom.Content ensures all of the content is visible, Zoom.static uses a static zoom factor of your choosing, and Zoom.x makes a specific number of x units visible. Zoom.min takes two other Zooms and uses the smaller of the two factors, and Zoom.max is the opposite of Zoom.min. You can also create your own Zoom implementations.
- Compose
- Views
The isZoomEnabled and autoScaleUp parameters of CartesianChartHost have been removed in favor of a zoomState parameter. This takes a VicoZoomState instance, which you can create via rememberVicoZoomState:
CartesianChartHost(zoomState = rememberVicoZoomState(...), ...)
The isZoomEnabled and autoScaleUp properties of CartesianChartView have been removed in favor of a zoomHandler property. This stores a ZoomHandler instance, which you can create via the constructor:
cartesianChartView.zoomHandler = ZoomHandler(...)
You can toggle zoom and specify the initial, minimum, and maximum Zooms. In particular, to get the behavior of AutoScaleUp.None, set initialZoom to Zoom.static(1f). For AutoScaleUp.Full, you’d use Zoom.max(Zoom.static(), Zoom.Content), but this is the default, so no need to specify it explicitly. Another addition is the ability to read the current zoom factor.
The default minimum and maximum Zooms are now dynamic, which resolves an issue where CartesianCharts couldn’t be zoomed out far enough, among others. We’ve added state restoration, so CartesianCharts’ zoom factors are persisted across configuration changes (e.g., on screen rotation).
Miscellaneous
Several APIs that shouldn’t be exposed have been hidden. Some other APIs have been marked as deprecated because they’re being renamed or are duplicates of other APIs. Follow the instructions in the deprecation messages to migrate.
This is unlikely to affect you, but MeasureContext no longer extends Extras, which has been removed. Instead, it has an extraStore field. The ExtraStore accessible via this field can be used for the same purposes as Extras. As part of this change, the string keys in the MarkerCorneredShape companion object (TICK_X_KEY and TICK_POSITION_KEY) have been replaced with ExtraStore keys (tickXKey and tickPositionKey).